Layer 2 Solutions have emerged as a promising alternative in the blockchain space, particularly as developers seek to enhance scalability and reduce costs without creating entirely new blockchains. These solutions, often referred to as L2s, sit on top of existing ones like Ethereum, creating a more efficient environment for transactions and smart contracts.
Table of Contents
- What Are Layer 1 and Layer 2 Solutions?
- The Benefits of Layer 2 Solutions
- Challenges Faced by Layer 1 Solutions
- Layer 2 Solutions: A Path Forward
- Frequently Asked Questions
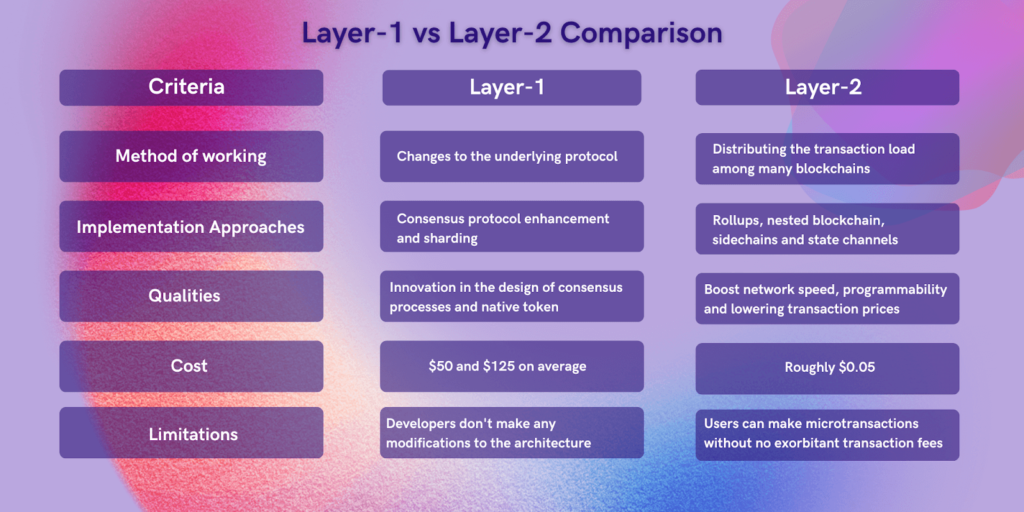
What Are Layer 1 and Layer 2 Solutions?
Layer 1 (L1) refers to the foundational blockchain protocols like Bitcoin and Ethereum. They are the base layer where all transactions are validated and recorded. On the other hand, Layer 2 solutions are built on top of Layer 1 blockchains and are designed to improve transaction speeds and reduce costs.
Key Differences Between Layer 1 and Layer 2
- Foundation vs. Flexibility: L1s provide the core functionality of a blockchain, while L2s offer greater flexibility for developers to build applications without the complexities of starting a new blockchain.
- Interoperability Challenges: New L1 blockchains often face issues with interoperability, leading to liquidity fragmentation where assets are scattered across multiple blockchains. L2s, however, come with built-in bridges that work seamlessly with their parent blockchain’s security.
The Benefits of Layer 2 Solutions
Layer 2 solutions offer several advantages over Layer 1 blockchains:
- Enhanced Scalability: L2s allow for higher transaction throughput by processing transactions off-chain and then settling them on-chain.
- Cost Efficiency: By reducing the load on the main blockchain, L2s can significantly lower transaction fees.
- Improved User Experience: Faster transaction times and lower costs contribute to a smoother user experience, which is crucial for mass adoption of blockchain technology.

Challenges Faced by Layer 1 Solutions
While Layer 1 blockchains have their merits, they also face significant challenges:
- Interoperability Issues: Many L1 blockchains struggle to communicate with each other, which complicates the movement of assets.
- Liquidity Fragmentation: As assets become scattered across various L1s, it creates hurdles for users trying to transfer value.
Layer 2 Solutions: A Path Forward
Layer 2 solutions present a way to address the shortcomings of Layer 1 blockchains. They offer a more flexible and efficient approach to transaction processing without the need for entirely new blockchains. By building on existing networks, L2s can enhance scalability while ensuring security and interoperability.
Conclusion
The ongoing debate in the blockchain community revolves around whether to continue developing new Layer 1 blockchains or to focus on improving Layer 2 solutions. As the industry evolves, it’s clear that Layer 2 solutions like rollups and sidechains are gaining traction due to their ability to enhance transaction speeds and reduce costs without the overhead of starting from scratch.
Frequently Asked Questions
A. The main advantage is the ability to enhance scalability and reduce transaction costs while leveraging the security of the underlying Layer 1 blockchain.
A. L2s often come with built-in bridges that facilitate smoother interactions with their parent L1 blockchains, reducing liquidity fragmentation.
A. New L1s often face challenges with interoperability and liquidity, making it difficult for users to move assets efficiently.
Made with VideoToBlog

![Unlocking the Power of Fan Tokens: A Step-by-Step Guide [Part 1]](https://coinqlo.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/Depositphotos_503743464_L-870x570.jpg)
![Creating Your Own Fan Token: A Step-by-Step Guide [Part 2]](https://coinqlo.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/0a6e2bc8-7679-4f96-8e43-ff7dfa1eca25-870x570.png)